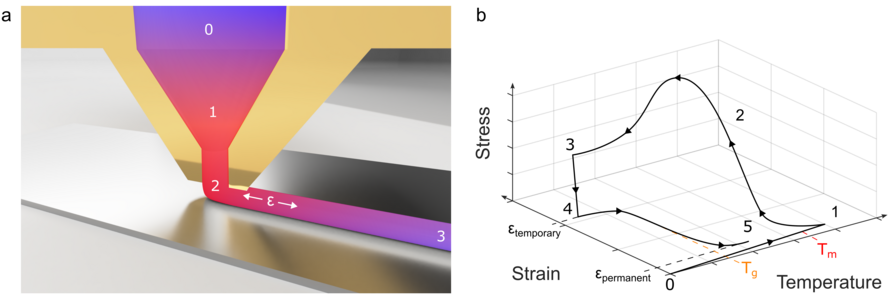
Fused deposition modeling (FDM)-based 4D printing enables the cost-effective production of programmable and shape-changing structures. However, the technology is still limited by an incomplete understanding of how printing settings influence internal stresses and final shape changes. In this study, we investigate how key printing parameters affect material flow and temperature during filament deposition. Printing forces were measured experimentally and compared with high-fidelity numerical simulations. The results show that nozzle temperature, printing speed, and material flow rate strongly influence printing forces and the internal structure of the printed filament. Understanding these relationships helps to better control the printing process. The findings contribute to improving the reliability of 4D printing and support the development of smart, adaptive structures.
F. Cerbe, F. A. González, M. Sinapius, M. Behr, S. Elgeti
Printing force analysis in FDM-based 4D printing of singular lines: A numerical and experimental study
Additive Manufacturing, 118, 105108 (2026) [Link]