Dive into the depths of marine aquaculture dynamics! The surge in demand for marine proteins, coupled with stagnant wild fish catch, propels the growth of bivalve farming. But with near-shore space running scarce, research is venturing offshore.
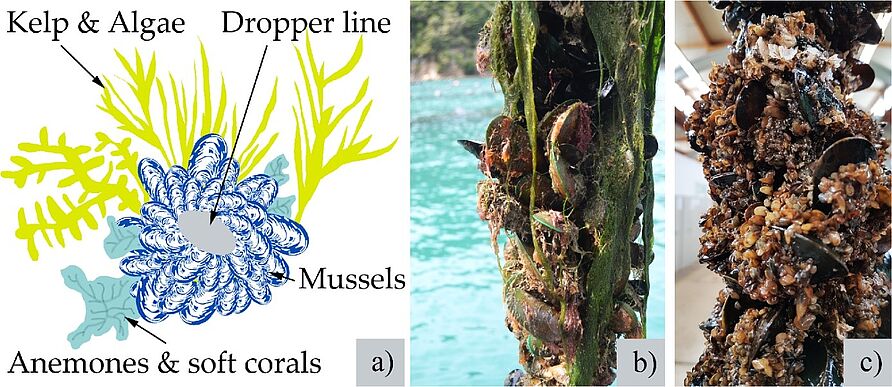
In our study, using cutting-edge results from our large-scale wave tank facility (GWK), a novel numerical model to estimate the forces on submerged dynamically moving mussel dropper lines is introduced. Drag and inertia coefficients (CD = 1.1 and CM = 1.7, respectively) are recommended for modeling. The numerical model, based on a modified Morison equation, explicitly considers mussel dropper line displacement for the first time.
Aquaculture-related parameter influences are discussed, providing engineering insights for optimal mussel aquaculture placement in the water column.
Landmann, J., Flack, C., Kowalsky, U., Wüchner, R., Hildebrandt, A., Goseberg, N.
Hydrodynamic coefficients of mussel dropper lines derived from large-scale experiments and structural dynamics.
J. Ocean Eng. Mar. Energy (2023).
https://doi.org/10.1007/s40722-023-00306-w